Write your first workflow with Cadence
We have covered basic components of Cadence and how to implement a Cadence worker on local environment in previous blogs. In this blog, let's write your very first HelloWorld workflow with Cadence. I've started the Cadence backend server in background and registered a domain named test-domain. You may use the code snippet for the worker service in this blog. Let's first write an activity, which takes a single string argument and prints a log in the console.
func helloWorldActivity(ctx context.Context, name string) (string, error) {
logger := activity.GetLogger(ctx)
logger.Info("helloworld activity started")
return "Hello " + name + "!", nil
}
Then let's write a workflow that invokes this activity
func helloWorldWorkflow(ctx workflow.Context, name string) error {
ao := workflow.ActivityOptions{
ScheduleToStartTimeout: time.Minute,
StartToCloseTimeout: time.Minute,
HeartbeatTimeout: time.Second * 20,
}
ctx = workflow.WithActivityOptions(ctx, ao)
logger := workflow.GetLogger(ctx)
logger.Info("helloworld workflow started")
var helloworldResult string
err := workflow.ExecuteActivity(ctx, helloWorldActivity, name).Get(ctx, &helloworldResult)
if err != nil {
logger.Error("Activity failed.", zap.Error(err))
return err
}
logger.Info("Workflow completed.", zap.String("Result", helloworldResult))
return nil
}
Don't forget to register your workflow and activity to your worker in the init function.
func init() {
workflow.Register(helloWorldWorkflow)
activity.Register(helloWorldActivity)
}
Now restart your worker and you will only see logs like
2023-07-16T12:07:33.165-0700 INFO internal/internal_worker.go:834 Started Workflow Worker {"Domain": "test-domain", "TaskList": "test-worker", "WorkerID": "13585@uber-C02F18EQMD6R@test-worker@42f8a76f-cc42-4a0d-a001-7f7959d5d623"}
2023-07-16T12:07:33.175-0700 INFO internal/internal_worker.go:859 Started Activity Worker {"Domain": "test-domain", "TaskList": "test-worker", "WorkerID": "13585@uber-C02F18EQMD6R@test-worker@42f8a76f-cc42-4a0d-a001-7f7959d5d623"}
2023-07-16T12:07:33.175-0700 INFO cadence-worker/code.go:84 Started Worker. {"worker": "test-worker"}
Let's try to run a Cadence workflow using Cadence CLI.
cadence --env development --domain test-domain workflow start --et 60 --tl test-worker --workflow_type main.helloWorldWorkflow --input '"World"'
You should see the Hello World log such like
2023-07-16T12:09:11.858-0700 INFO cadence-worker/code.go:104 Workflow completed. {"Domain": "test-domain", "TaskList": "test-worker", "WorkerID": "13585@uber-C02F18EQMD6R@test-worker@42f8a76f-cc42-4a0d-a001-7f7959d5d623", "WorkflowType": "main.helloWorldWorkflow", "WorkflowID": "8cb7fb2a-243b-43f8-82d9-48d758c9d62f", "RunID": "3c070007-89c3-4e00-a039-19a86b2f9224", "Result": "Hello World!"}
Congratulations, you have successfully run your very first Cadence workflow.
For a bonus point, the Cadence team has also developed a demonstrative web dashboard to visualize the history of all workflows you have run when you start the Cadence server. Check http://localhost:8088 to see the dashboard like this.
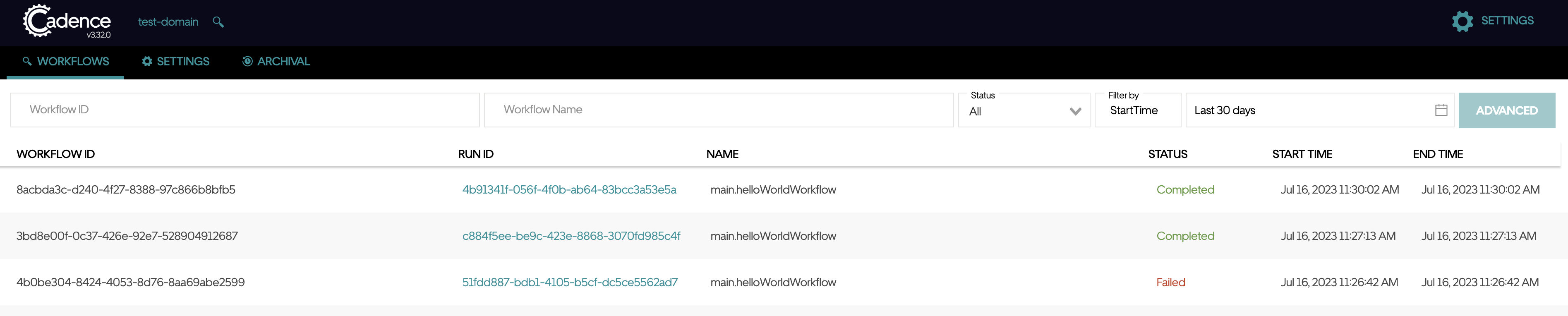
This web portal persists all historical workflow you have run recently. Search for the domain you used for this tutorial. In our case, type test-domain and hit enter. You may see a list of workflows with detailed information. Feel free to explore the web UI and raise your suggestions to our Github repo.
For the incoming blogs, we will cover more advanced topics and use cases with Cadence.
